Strong Nuclear Force
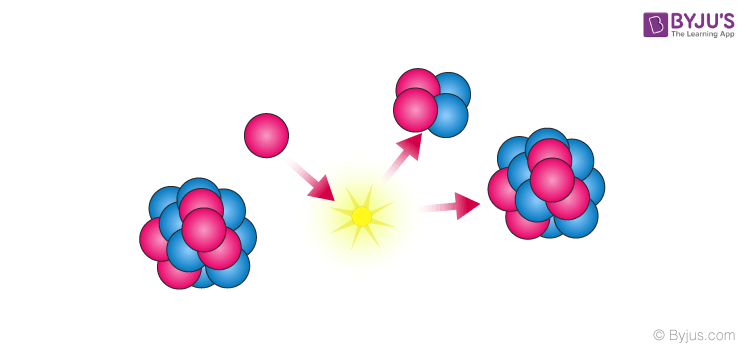
The strong nuclear force, also called the strong nuclear interaction, is the strongest of the four fundamental forces of nature. It's 6 thousand trillion trillion trillion (that’s 39 zeroes after.
Sorry, Energy Education does not support your browser version. Please switch browsers or upgrade Internet Explorer to version 8 or above to view this website properly.
The weak nuclear force (or just the weak force, or weak interaction) acts inside of individual nucleons, which means that it is even shorter ranged than the strong force. It is the force that allows protons to turn into neutrons and vice versa through beta decay. This keeps the right balance of protons and neutrons in a nucleus. The weak force is very important in the nuclear fusion that happens in the sun.[1] Nuclear fusion has also been created in laboratories, and that process requires the weak force to work too. See size of the universe for a list of visuals demonstrating how short ranged the weak force is.
As the name implies, the weak force is much weaker than the strong force, or the electromagnetic force, but it is quite a bit stronger than the gravitational force.
Gravitational force. All objects in the universe. Weak nuclear force. Very short, Sub-nuclearsize (-10-16 m) Some elementary particles, particularly electron and neutrino. Electromagnetic force. Charged particles. Strong nuclear force. Short, nuclear size (-10-15 m) Nucleons, heavier. The strong nuclear force is a force between the fundamental particles that constitute the nucleus. It can be between two protons, two neutrons, or a proton and a neutron. The interaction between quarks, which are the smallest particles that constitute protons and neutrons, is also mediated through the strong force. Strong force, a fundamental interaction of nature that acts between subatomic particles of matter. The strong force binds quarks together in clusters to make more-familiar subatomic particles, such as protons and neutrons. It also holds together the atomic nucleus and underlies interactions between all particles containing quarks. Strong force: This is a short-range attractive force. 'Short range' refers to the fact that the force dies off exponentially in distance. This means that a nucleon is only affected by the strong force of its nearest neighbors. However, within that distance of less than 2.0 E-15 m, it overwhelms the other forces.
Modern physics has unified the electromagnetic and weak forces into the electroweak force. There is a continued effort to try to unify all of the forces in a grand unified theory.
Fully understanding the weak force takes many years of study, but some fun places to start include hyperphysics or the blog of Prof. Matt Strassler.
Below is the Scishow's series on fundamental forces part 2, the weak force:
For Further Reading
To learn about the other forces, please see the following pages:
- Or explore a random page
References
- ↑Sears and Zemanski's University Physics, 13th edition by Young and Freedman. Addison Wesley, 2010. Chapter 44, pg 1491.
Authors and Editors
Sarjana Amin, Allison Campbell, Jordan Hanania, Kailyn Stenhouse, Jason Donev
Last updated: January 31, 2020
Get Citation
Also found in: Thesaurus, Acronyms, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
strong nuclear force
n.Strong Nuclear Force Ppt
strong nuclear force
 (strông)
(strông)Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Link to this page:
Strong Nuclear Force Meaning
Strong Nuclear Force Relative Strength
